Glaucoma Testing and Early Detection: Why It’s Crucial for Vision Health
Glaucoma is known as the “silent thief of sight” because it develops gradually and often shows no symptoms until significant vision loss occurs. Once the damage is done, it cannot be reversed—making early detection through glaucoma testing critical for preserving eyesight.
If left untreated, glaucoma can lead to permanent blindness. However, with routine eye exams and early intervention, it is possible to slow its progression and protect your vision.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what glaucoma is, why early testing is crucial, who is at risk, and the best treatment options available.
1. What is Glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that damage the optic nerve, the crucial link between the eye and the brain. This damage is often caused by increased intraocular pressure (IOP)—when fluid builds up in the eye and cannot drain properly.
Over time, this pressure damages the optic nerve, leading to gradual loss of vision. If detected too late, glaucoma can cause irreversible blindness.
Types of Glaucoma
There are several types of glaucoma, with the most common being:
1. Open-Angle Glaucoma (OAG) – The Most Common Form
- Occurs when fluid drains too slowly from the eye, increasing pressure.
- Develops gradually, often without noticeable symptoms.
- The leading cause of blindness worldwide.
2. Angle-Closure Glaucoma (ACG) – A Medical Emergency
- Occurs when the drainage angle in the eye suddenly becomes blocked.
- Causes rapid vision loss, severe pain, nausea, and redness.
- Requires immediate medical attention to prevent blindness.
3. Normal-Tension Glaucoma (NTG)
- Damage to the optic nerve even with normal eye pressure.
- Thought to be linked to poor blood flow to the optic nerve.
- Often diagnosed through glaucoma testing and early detection.
📌 Related Resource: National Eye Institute: Types of Glaucoma
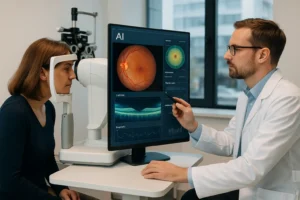
2. Why Early Detection Through Glaucoma Testing is Critical
Glaucoma can cause permanent vision loss before symptoms appear. Unlike other eye conditions, glaucoma damages peripheral vision first, meaning you may not notice vision loss until it is advanced.
The Role of Glaucoma Testing in Early Detection
- Tonometry Test – Measures eye pressure (IOP).
- Ophthalmoscopy – Examines the optic nerve for damage.
- Visual Field Test (Perimetry) – Checks for blind spots in peripheral vision.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) – Uses imaging technology to detect early optic nerve changes.
These tests help diagnose glaucoma before vision loss occurs, allowing for early treatment and better outcomes.
📌 Related Resource: American Academy of Ophthalmology: Glaucoma Testing
3. Who is at Risk for Glaucoma?
While anyone can develop glaucoma, some people are at higher risk. You should get regular glaucoma testing if you:
- Are over the age of 40.
- Have a family history of glaucoma.
- Have high eye pressure (IOP).
- Are African American, Hispanic, or Asian (higher genetic risk).
- Have diabetes or hypertension.
- Have severe nearsightedness (myopia).
- Have had eye injuries or long-term steroid use.
📌 Related Resource: Glaucoma Research Foundation: Risk Factors
4. Treatment Options for Glaucoma
Although glaucoma damage cannot be reversed, early treatment can slow or prevent further vision loss.
a) Prescription Eye Drops – The First Line of Defense
- Lowers eye pressure by reducing fluid production or improving drainage.
- Must be used daily to be effective.
b) Laser Therapy (Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty – SLT)
- Helps fluid drain more efficiently from the eye.
- Often used when eye drops are not enough.
c) Surgery for Severe Glaucoma
- Trabeculectomy: Creates a new drainage channel for fluid.
- Glaucoma Drainage Implants: Small devices that help reduce pressure.
d) Lifestyle Changes to Support Eye Health
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in omega-3s, vitamin C, and antioxidants.
- Exercise regularly to promote healthy blood flow to the optic nerve.
- Avoid smoking and limit caffeine intake.
📌 Find a Glaucoma Specialist Near You: American Optometric Association – Find a Doctor
5. How Often Should You Get Glaucoma Testing?
- Under 40 years old: Every 2-4 years.
- Ages 40-54: Every 1-3 years.
- Ages 55-64: Every 1-2 years.
- 65 and older: Annually.
If you are high-risk, annual glaucoma testing is essential to prevent vision loss.
📌 Related Resource: Prevent Blindness: Glaucoma Screening Guidelines
Final Thoughts
Glaucoma testing and early detection are crucial for preserving vision and preventing blindness. Because glaucoma has no early warning signs, regular eye exams are the only way to detect and treat it early.
If you are at risk or haven’t had an eye exam recently, schedule a glaucoma screening as soon as possible to protect your sight.
For more glaucoma resources, visit the Glaucoma Research Foundation or the National Eye Institute.